GST/GPX/GR
Glutathione (GSH) plays a key role in the antioxidant defense of the liver. GSH can scavenge free radicals and toxic compounds, as well as modulate the inflammatory and immune response. GSH also participates in the network that regulates cell survival, necrosis, and apoptosis.
The glutathione system consists of several enzymes that are involved in the synthesis, metabolism, and regulation of GSH. These enzymes include glutathione synthetase (GS), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and glutaredoxin (Grx). GS catalyzes the formation of GSH from its precursor molecules. GR reduces the oxidized form of GSH (GSSG) back to GSH using NADPH as a cofactor. GPx uses GSH to reduce hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxides to water and alcohols, respectively. GST conjugates GSH with electrophilic substrates, such as xenobiotics, drugs, and carcinogens, facilitating their excretion. Grx catalyzes the reduction of protein disulfides and mixed disulfides between proteins and GSH.
The glutathione system is important for maintaining the redox balance in the kidney and detoxifying capacity of the liver. The liver is particularly exposed to oxidative stress and toxic insults due to its metabolic functions and its role in filtering the blood. Several liver diseases, such as viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcoholic liver disease, chronic cholestatic injury, ischemia/reperfusion damage, and hepatocellular carcinoma, are associated with altered levels of GSH and glutathione-related enzymes.
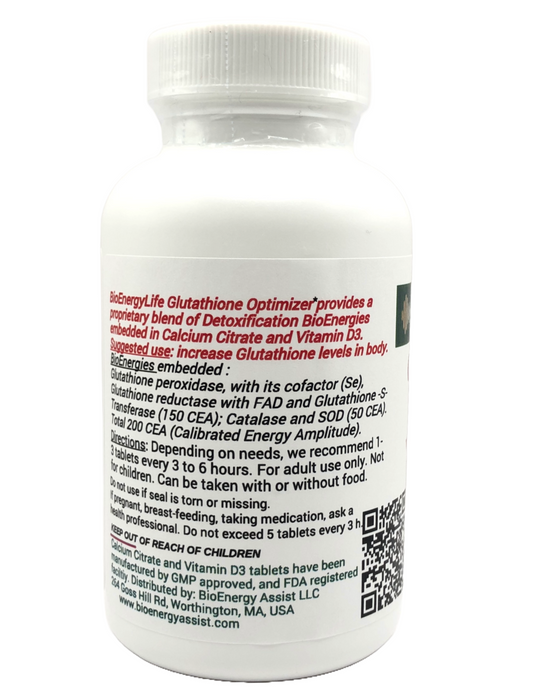
Our Glutathione products assist the GST, GPx and GR enzymes in the glutathione system to help maintain redox balance and detoxification in cells, and particularly in the liver and kidney.*
- Featured
- Best selling
- Alphabetically, A-Z
- Alphabetically, Z-A
- Price, low to high
- Price, high to low
- Date, old to new
- Date, new to old